 CT is a dianostic imaging technique which creates transverse section images of the body using an x-ray source which rotates around the body and focuses x-rays on a ”slice” of the body. CT is a dianostic imaging technique which creates transverse section images of the body using an x-ray source which rotates around the body and focuses x-rays on a ”slice” of the body.
The x-ray energy is absorbed differently in the tissue and the non-absorbed x-rays are detected by receptors and converted into a computer image.
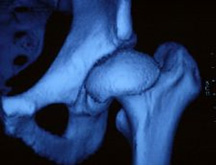
The transverse section images can be converted into three-dimensional reconstruction images which make it easier to make a diagnosis and a treatment plan.
CT is also used for monitoring the effect of the treatment. CT induces a larger x-ray impact on the patient depending on which body part is scanned.
At the clinic our Orthopaedic Surgical Research Group has, with great success, used multi slice CT for the evaluation of seven relevant acetabular angles and the covering of caput femoris at pre-surgical planning of joint preservation surgery on patients with hip dysplasia. |